Cybersecurity in the era of cloud computing

Cybersecurity in the era of cloud computing emphasizes the need for advanced protection measures, including encryption, AI integration, and a zero trust model to safeguard sensitive data against evolving threats.
Cybersecurity in the era of cloud computing has become a pressing concern for businesses and individuals alike. With the surge in data storage solutions, understanding how to protect your information is more vital than ever.
Understanding the basics of cloud security
Understanding cloud security is essential in today’s digital landscape. As more businesses shift to the cloud, it becomes critical to know how to protect your valuable information.
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security involves a set of policies, technologies, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure associated with cloud computing. It isn’t just about securing the data itself; it’s also about ensuring compliance and maintaining privacy.
Key Components of Cloud Security
There are several important elements to consider when discussing cloud security:
- Data Encryption: This protects data both at rest and in transit.
- Identity Management: Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access.
- Access Control: Setting permissions and restrictions based on user roles.
- Regular Audits: Conducting assessments to ensure compliance with security policies.
By focusing on these components, organizations can improve their overall security posture in the cloud environment. Furthermore, as cyber threats evolve, so too must our approaches to cloud security. Regularly updating security protocols is vital to safeguard sensitive information.
Throughout this process, it’s important for users to become familiar with tools and resources available for securing their cloud environments. Understanding how to leverage these resources can lead to better security practices and, ultimately, peace of mind.
Common threats in cloud computing
Understanding the common threats in cloud computing is crucial for maintaining data security. As companies transition to the cloud, they face various risks that can compromise their data and systems.
Data Breaches
A significant threat in the cloud is a data breach. This occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive data. These breaches can result from weak passwords, unencrypted data, or inadequate security measures.
Account Hijacking
Account hijacking is another prevalent issue. Attackers can take over user accounts, leading to unauthorized access to vital information. This often happens through phishing attacks or by exploiting weak authentication methods.
- Phishing: Attackers trick users into revealing their credentials.
- Insecure APIs: Poorly designed application interfaces can expose vulnerabilities.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors with malicious intent can misuse access.
Additionally, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks target cloud services by overwhelming them with traffic. This can disrupt service availability and lead to significant downtime for businesses.
It’s essential for organizations to recognize these threats and implement robust security measures. This includes regularly updating security policies, conducting security audits, and training employees on recognizing potential risks.
Awareness and proactive defense strategies are key to safeguarding against these common threats in the cloud. By being informed and prepared, businesses can better protect their data and ensure seamless cloud operations.
Best practices for data protection
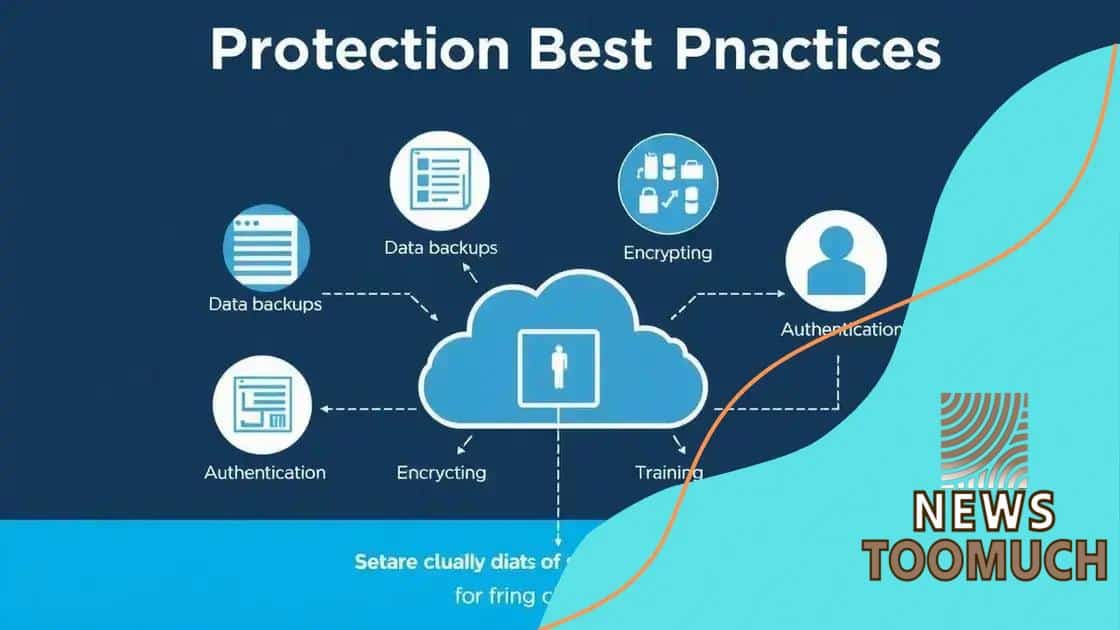
Implementing best practices for data protection is crucial for securing sensitive information in the cloud. As cyber threats evolve, organizations must stay ahead by adopting effective security measures.
Regular Data Backups
One of the foremost practices is to conduct regular data backups. This ensures that in the event of a breach or data loss, your organization can swiftly recover critical information without excessive downtime.
Strong Authentication Methods
Utilizing strong authentication methods can greatly enhance security. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of protection. By requiring more than one form of verification, it reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Use unique passwords: Encourage the use of complex, unique passwords for all accounts.
- Limit access: Ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Monitor access: Regularly review access logs for any suspicious activity.
It is also vital to encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to attackers. Additionally, encrypting backups adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to access critical information.
Another key aspect of data protection is employee training. Regularly educating staff about potential threats and safe practices can significantly decrease the likelihood of human error leading to data breaches. Training should include recognizing phishing attempts and understanding the importance of secure data handling.
Lastly, maintaining up-to-date software and security patches is essential. Regular software updates can protect against vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit. By ensuring that all systems are current, organizations can shield themselves from many common threats.
The role of encryption in cloud storage
The role of encryption in cloud storage is critical for protecting sensitive data. As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, encryption serves as a vital defense against unauthorized access.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting information into a code, making it unreadable without a key or password. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains secure. In cloud storage, this means that sensitive files like financial records or personal information are safeguarded.
Types of Encryption
There are two main types of encryption used in cloud storage:
- At-rest Encryption: This protects data stored on servers. Data remains encrypted when it is saved and only decrypted when accessed by authorized users.
- In-transit Encryption: This secures data as it moves between the user and the cloud. It prevents interception during upload or download.
By implementing both types, cloud providers can offer robust security to clients. Encryption plays a vital role in compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA, which require organizations to protect personal and sensitive data.
Adopting encryption standards such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) ensures a high level of security. It is crucial for businesses to verify that their cloud provider uses strong encryption protocols. This not only protects data but also enhances trust between the provider and users.
In addition to securing data, encryption also aids in establishing data integrity. This means that users can be confident that their information has not been altered during storage or transmission. Effective use of encryption makes it significantly harder for cybercriminals to access and misuse sensitive data.
Future trends in cybersecurity and cloud
The future trends in cybersecurity and cloud are evolving rapidly. As technology advances, organizations must adapt to new threats and changes in security measures. Understanding these trends is essential to protect sensitive information.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are becoming vital in cybersecurity. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, helping to identify threats before they cause damage. AI can also automate responses to potential breaches, reducing the time it takes to respond to incidents.
Zero Trust Security Models
The zero trust model is gaining traction. This approach assumes that threats can be both inside and outside the network. Thus, every access request must be verified. By continuously validating users and devices, organizations can enhance their security posture.
- Multi-factor authentication: Adding layers of security beyond just passwords.
- Granular access controls: Limiting user access based on specific needs.
- Real-time monitoring: Keeping an eye on user activity for unusual behaviors.
Another trend is the shift to cloud-native security solutions. As more businesses move their operations to the cloud, integrating security directly into cloud services is becoming common. This allows for better protection of data stored in cloud environments.
Furthermore, the rise of IoT (Internet of Things) devices poses new challenges for cybersecurity. With more connected devices, the number of potential entry points for hackers increases. Businesses must ensure that these devices are secure and monitored to prevent breaches.
Finally, adherence to regulations will continue to shape the future of cybersecurity. Companies need to comply with laws related to data protection and privacy. Staying informed of regulatory changes will be critical for maintaining compliance and protecting consumer trust.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Cybersecurity and Cloud Computing
What is the importance of encryption in cloud storage?
Encryption protects sensitive data by making it unreadable to unauthorized users, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains secure.
How can AI enhance cybersecurity measures?
AI can analyze large amounts of data quickly to detect threats, automate incident responses, and improve the overall security posture of an organization.
What does a zero trust security model entail?
A zero trust model requires that every access request must be verified, assuming that threats can exist both inside and outside the network.
What challenges do IoT devices pose in cybersecurity?
IoT devices can serve as entry points for cyber attacks, making it crucial to secure them properly to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.





